Exploring the world of fermented foods sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality. From historical significance to health benefits, this exploration delves into the diverse and fascinating realm of fermented foods.
The Importance of Fermented Foods
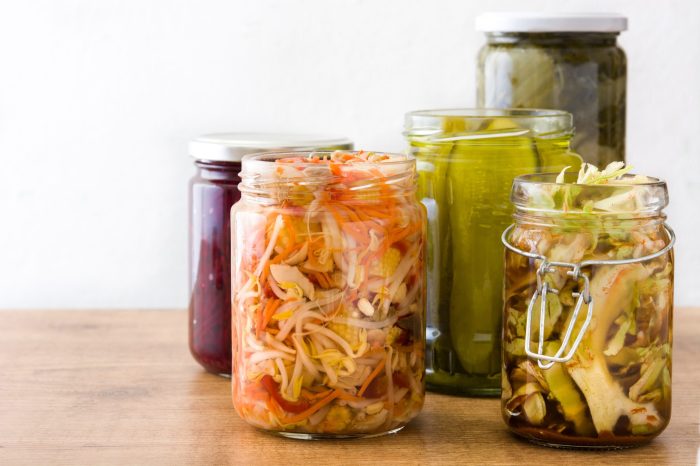

Fermented foods have been a part of human diet for thousands of years and have significant health benefits. The process of fermentation involves the use of bacteria, yeast, or other microorganisms to break down sugars and starches in foods, creating beneficial compounds like probiotics, enzymes, and B vitamins.
Health Benefits of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods are known to promote gut health by introducing beneficial bacteria into the digestive system. These probiotics help balance the gut microbiome, improve digestion, and boost the immune system. Additionally, fermented foods can increase the bioavailability of nutrients in the food, making it easier for the body to absorb essential vitamins and minerals.
- Sauerkraut: A popular fermented food made from cabbage that is rich in probiotics and vitamin C.
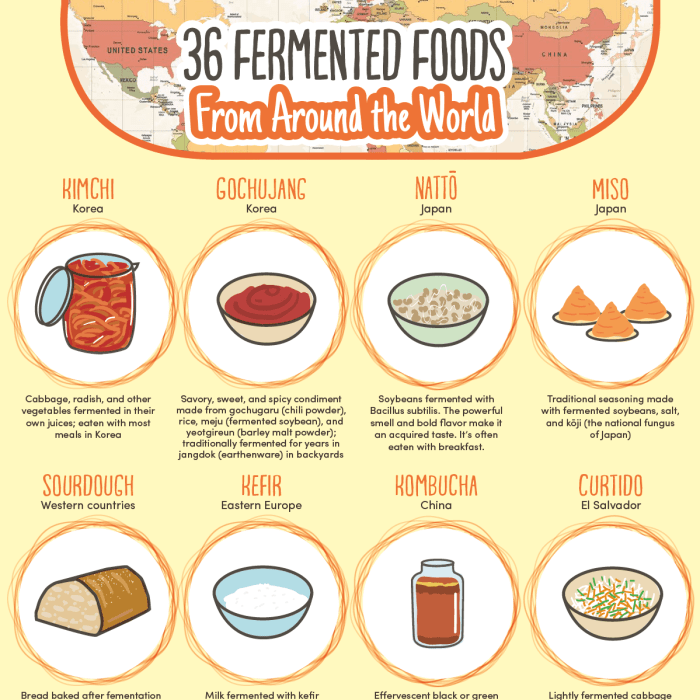
- Kimchi: A traditional Korean dish made from fermented vegetables like cabbage and radishes, known for its probiotic content and spicy flavor.
- Kombucha: A fermented tea beverage that contains probiotics and antioxidants, which may help improve digestion and boost the immune system.
- Yogurt: A dairy product made by fermenting milk with live bacteria cultures, known for its probiotic properties and calcium content.
Historical Significance of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods have a long history in various cultures around the world. In ancient times, fermentation was used as a method of food preservation before the advent of refrigeration. Many traditional fermented foods are still consumed today as a way to preserve cultural heritage and benefit from their nutritional value.
- Kimchi in Korea: Kimchi has been a staple in Korean cuisine for centuries, with each family having its own recipe and fermentation techniques passed down through generations.
- Sauerkraut in Germany: Sauerkraut has been consumed in Germany since the Roman era and was traditionally used to prevent scurvy among sailors on long sea voyages.
- Miso in Japan: Miso, a fermented soybean paste, has been a key ingredient in Japanese cuisine for over a thousand years, providing a rich umami flavor and probiotic benefits.
The Science Behind Fermentation

Fermentation is a metabolic process that involves the breakdown of carbohydrates by microorganisms like bacteria, yeast, or fungi in the absence of oxygen. This process helps to preserve food, enhance flavor, and increase the nutritional value of certain foods.
Fermentation Process and Transformation of Food
During fermentation, microorganisms convert sugars and other carbohydrates into compounds like alcohol, organic acids, and gases. This process not only helps to break down complex nutrients into simpler forms but also produces unique flavors and textures in the final product. For example, in the case of yogurt production, lactic acid bacteria ferment lactose in milk to produce lactic acid, which gives yogurt its tangy taste and thick consistency.
Role of Probiotics in Fermented Foods and Gut Health
Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. Many fermented foods, such as yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut, contain probiotic strains that can help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. These beneficial bacteria can improve digestion, boost the immune system, and even reduce inflammation in the gut. Regular consumption of probiotic-rich fermented foods can contribute to overall gut health and well-being.
Nutritional Differences Between Fermented and Non-Fermented Foods
Fermentation can enhance the nutritional profile of foods by increasing the availability of certain nutrients and improving digestibility. For instance, fermented dairy products like yogurt and kefir are easier to digest for individuals with lactose intolerance due to the fermentation process that breaks down lactose. Fermented foods also tend to be rich in vitamins, minerals, and beneficial compounds like antioxidants. On the other hand, non-fermented foods may lack these additional nutrients and health-promoting properties found in fermented alternatives.
Global Varieties of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods have been a staple in various cuisines around the world for centuries, offering unique flavors and beneficial probiotics. Let’s explore traditional fermented foods from different countries and regions, highlighting the ingredients, techniques, and cultural significance involved.
Kimchi (South Korea)
Kimchi is a well-known Korean side dish made of fermented vegetables, typically napa cabbage and radishes, seasoned with ingredients like ginger, garlic, and red pepper flakes. The fermentation process involves salting the vegetables to draw out moisture, then mixing them with the seasoning paste before allowing them to ferment. Kimchi plays a significant role in Korean culture and is often served with meals as a source of probiotics and vitamins.
Sauerkraut (Germany)
Sauerkraut is a fermented cabbage dish that originated in Germany. Cabbage is thinly sliced, salted, and fermented in its own juices or brine, creating a tangy and crunchy condiment. Sauerkraut is commonly used in German cuisine, especially as a topping for sausages or as a side dish. It is rich in probiotics and vitamin C, making it a popular choice for gut health and immune support.
Kombucha (China)
Kombucha is a fermented tea beverage that traces its roots back to ancient China. It is made by fermenting sweetened tea with a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) to produce a slightly effervescent drink. Kombucha is known for its tangy flavor and health benefits, including improved digestion and immune support. It has gained popularity worldwide as a refreshing and probiotic-rich beverage.
Miso (Japan)
Miso is a traditional Japanese seasoning made by fermenting soybeans with salt and koji (a type of mold). The mixture is aged for several months to years, resulting in a paste with a savory and umami-rich flavor. Miso is used in a variety of Japanese dishes, such as miso soup, marinades, and dressings. It is valued not only for its unique taste but also for its probiotic content and potential health benefits.
Fermentation at Home

Fermenting foods at home can be a fun and rewarding process. Not only does it allow you to create unique and flavorful dishes, but it also provides you with the opportunity to explore the world of fermentation in your own kitchen. However, it is important to follow proper guidelines to ensure that your fermentation process is safe and successful.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fermenting Foods at Home
- Choose the right vegetables or ingredients for fermentation, such as cabbage for making sauerkraut or cucumbers for pickles.
- Clean and sanitize all utensils, jars, and equipment to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Cut or shred the vegetables to the desired size and mix them with salt or a brine solution to kickstart the fermentation process.
- Place the vegetables in a clean, airtight container and ensure that they are fully submerged in the brine to prevent mold growth.
- Store the container in a cool, dark place and allow the vegetables to ferment for the recommended time, typically 1-4 weeks depending on the recipe.
- Check the vegetables regularly for any signs of mold or spoilage, and taste them periodically to monitor the fermentation process.
- Once the vegetables reach the desired level of fermentation, transfer them to the refrigerator to slow down the process and enjoy your homemade fermented foods!
Tips for Beginners Starting Their Fermentation Journey
- Start with simple recipes like sauerkraut or pickles before experimenting with more complex fermentations.
- Use high-quality ingredients and ensure that all equipment is clean and sanitized to prevent contamination.
- Keep a fermentation journal to track your recipes, fermentation times, and flavor profiles for future reference.
- Join online fermentation communities or workshops to learn from experienced fermenters and get tips and advice for your own fermentation projects.
Common Troubleshooting Issues when Fermenting Foods at Home
- If you see mold on the surface of your fermenting vegetables, remove it immediately and ensure that the rest of the batch is submerged in the brine to prevent further contamination.
- If your fermented foods develop an off-putting smell or taste, it may indicate that harmful bacteria have taken over. In this case, it is best to discard the batch and start fresh with a new recipe.
- Inconsistent temperatures or exposure to light can affect the fermentation process. Make sure to store your fermenting foods in a stable environment to maintain a successful fermentation.
Health Benefits of Fermented Foods
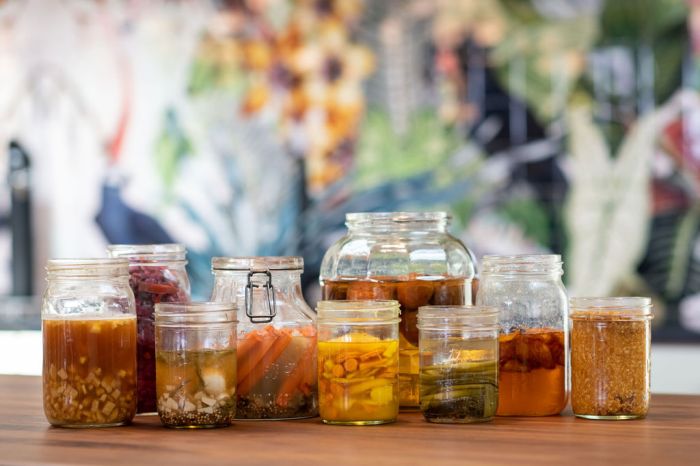

Fermented foods have been known for their numerous health benefits, ranging from improved digestion to enhanced immune system support. These benefits can be attributed to the unique way in which fermentation transforms foods, making them more nutritious and easier to digest.
Improved Digestion
- Fermented foods contain probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that help maintain a healthy gut microbiome.
- Probiotics in fermented foods can aid in digestion by breaking down food components that the body may have difficulty digesting on its own.
- Consuming fermented foods regularly can help alleviate digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and constipation.
Immune System Support, Exploring the world of fermented foods
- Probiotics found in fermented foods can help strengthen the immune system by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- A healthy gut microbiome is essential for overall immune function, as it helps protect the body against harmful pathogens and infections.
- Regular consumption of fermented foods may reduce the risk of certain immune-related conditions, such as allergies and autoimmune diseases.
Nutrient Absorption and Overall Well-being
- Fermentation can increase the bioavailability of nutrients in foods, making them easier for the body to absorb.
- Enhanced nutrient absorption can lead to improved overall well-being, as the body is better able to utilize the essential vitamins and minerals present in fermented foods.
- Some fermented foods, such as kimchi and kefir, are rich in antioxidants and other beneficial compounds that can contribute to better health outcomes.
Scientific Studies Supporting the Benefits
- A study published in the journal Nutrients found that consuming probiotic-rich fermented foods can help improve digestion and alleviate symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders.
- Research published in Frontiers in Microbiology suggests that fermented foods can positively impact immune function by modulating the gut microbiota.
- Another study in the Journal of Applied Microbiology highlights the role of fermented foods in promoting overall well-being through enhanced nutrient absorption and gut health.
End of Discussion: Exploring The World Of Fermented Foods
As we conclude our journey through the world of fermented foods, we are reminded of the rich tapestry of flavors, cultures, and health benefits that fermentation brings. This exploration has highlighted the importance of this age-old practice in nourishing both body and soul, inviting us to savor the global varieties of fermented delights.
In order to achieve the perfect steak on the grill, it is essential to follow certain tips and techniques. One crucial tip is to properly season the steak before grilling it. This article on Tips for achieving the perfect steak on the grill provides detailed instructions on how to marinate and season your steak for optimal flavor and tenderness.
When it comes to making a delicious homemade chicken noodle soup, having the right recipe is key. This homemade chicken noodle soup recipe offers a step-by-step guide on how to prepare this comforting and nourishing dish. From selecting the best ingredients to cooking techniques, this recipe has got you covered.
Properly seasoning a cast iron skillet is essential for maintaining its non-stick surface and preventing rust. This detailed guide on how to properly season a cast iron skillet provides tips on the best oils to use, the correct seasoning process, and how to care for your skillet to ensure it lasts for years to come.